
Mandelic Acid: Benefits, Usage, and Skincare Tips for Best Results
Table of content
Introduction
In the skincare industry, Mandelic Acid is becoming a “holy grail” for sensitive skin thanks to its gentle yet effective chemical exfoliation. Belonging to the Alpha Hydroxy Acid (AHA) family, this acid is derived from bitter almonds and is notable for its large molecular size, which allows it to penetrate the skin more slowly, reducing the risk of irritation compared to other AHAs like Glycolic Acid or Lactic Acid.
If you’ve heard of chemical exfoliants but are worried about redness or peeling, Mandelic Acid serums and exfoliant products can be a great option. In this article, LùVaîi will help you understand Mandelic Acid benefits, compare it with other acids, and guide you on how to use it correctly to maximize its advantages for your skin.
Origin and Characteristics of Mandelic Acid
- Origin: Extracted from bitter almonds.
- Large molecule: Mandelic Acid’s molecular weight (~152.15 g/mol) is much larger than that of Glycolic Acid (~76.05 g/mol), leading to slower penetration.
- Mechanism of action: Mandelic Acid breaks the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, removing them to promote new cell turnover and brighten the skin.
- Key features: Gentle, minimal stinging sensation, suitable for most skin types, including sensitive skin.
.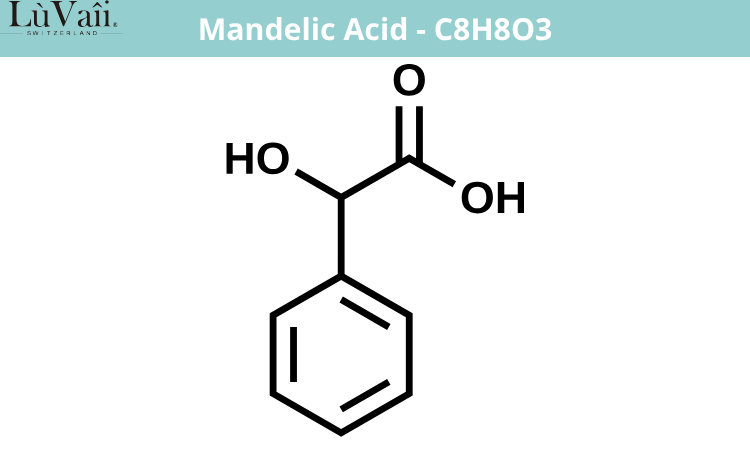
Công thức hoá học của Mandelic Acid _ C8H8O3
- Key features: Gentle, minimal stinging sensation, suitable for most skin types, including sensitive skin.
Key Benefits of Mandelic Acid
1. Chemical Exfoliation
Mandelic Acid exfoliant removes dead skin cells clinging to the skin’s surface, unclogs pores, and enhances absorption of other active ingredients. Regular exfoliation helps:
- Improve skin smoothness
- Boost the effectiveness of moisturizers and serums
- Prevent clogged pores
2. Acne Treatment Support
Mandelic Acid for acne works by killing acne-causing bacteria while removing excess oil and dead cells. It is particularly effective for:
- Mild to moderate inflammatory acne
- Closed comedones
- Reducing redness and swelling in acne-prone areas
3. Brightening Skin and Improving Pigmentation
With its ability to inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, Mandelic Acid for hyperpigmentation helps fade dark spots, freckles, and mild melasma. When included in a mandelic acid skincare routine, its brightening effects are enhanced.
4. Anti-Aging
Consistent use of Mandelic Acid serum can stimulate collagen production, reduce fine lines, and improve skin elasticity. This is why many dermatologists recommend it in anti-aging regimens.
5. Suitable for Sensitive Skin – A Major Plus
Thanks to its larger molecular size, Mandelic Acid penetrates the skin more slowly, reducing stinging or redness often experienced with AHAs. This is especially helpful for:
- Easily irritated skin: No strong peeling, minimal inflammation.
- Post-treatment skin: Safe to use after laser or strong chemical peels (only under medical advice).
- Dry, sensitive skin: Doesn’t strip excessive natural moisture.
Mandelic Acid vs Glycolic Acid vs Lactic Acid
| Criteria | Mandelic Acid | Glycolic Acid | Lactic Acid |
| Molecular size | Large | Small | Medium |
| Penetration rate | Slow | Fast | Medium |
| Irritation potential | Low | High | Low–Medium |
| Suitable for sensitive skin? | Yes | Rarely | Yes |
| Main benefits | Gentle exfoliation, acne care, brightening | Strong exfoliation, quick brightening | Gentle exfoliation, hydration |
How to Use Mandelic Acid Safely and Effectively
Choose the right concentration
- 5–10%: For beginners or sensitive skin.
- 15% and above: For skin used to AHAs, targeting pigmentation or acne scars.
2. Usage frequency
- Sensitive skin: 1–2 times/week
- Normal/combination skin: 2–3 times/week
- Always monitor skin’s reaction and reduce frequency if irritation occurs.
3. Pairing with other products
- Can pair with: Niacinamide, Hyaluronic Acid, hydrating serums.
- Avoid direct pairing with: Retinol, high-strength Vitamin C (L-Ascorbic Acid), other strong AHAs/BHAs — to reduce irritation risk.
4. Always use sunscreen
All AHAs increase sun sensitivity. SPF 30–50 sunscreen is a must when using Mandelic Acid.
Who Should and Shouldn’t Use Mandelic Acid?
Suitable for:
- Sensitive skin trying AHAs for the first time
- Oily skin, mild acne
- Uneven skin tone, post-acne dark spots
- Those combining mandelic acid and BHA for deeper acne treatment
Not suitable for:
- Skin with severe redness or eczema
- People allergic to bitter almonds
- Pregnant women (consult a doctor first)
Tips for Using Mandelic Acid on Sensitive Skin
- Patch test first: Apply to a small area (behind the ear, wrist) for 24–48 hours.
- Start with low concentration: Let skin gradually adapt, avoiding purging.
- Use at night: Avoid direct sunlight to minimize irritation.
- Moisturize: Prevent dehydration and help skin recover faster.
Mandelic Acid Products at LuVaii
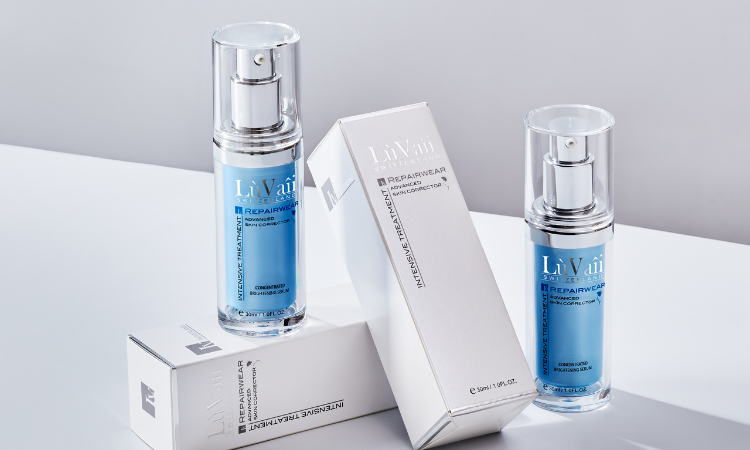

Concentrated Brightening Serum
If your skin struggles with dullness, dark spots, and rough texture but is sensitive to higher-strength AHAs or BHAs, try
Concentrated Brightening Serum.
With a larger molecular size, Mandelic Acid penetrates slowly and gently exfoliates dead skin cells, restoring radiance and smoothness. This formula also contains antioxidants to slow aging and keep skin soft, bright, and healthy.
Besides, the product also contains antioxidant ingredients, which help slow down the aging process, keep the skin smooth and healthy.
Combining Mandelic Acid with Other Ingredients
Compatible with:
- Niacinamide: Brightens and reduces inflammation
- Hyaluronic Acid: Deep hydration
- BHA (Salicylic Acid): Boosts acne treatment effectiveness (start with low frequency)
Avoid using together:
- Retinol: May cause irritation
- High-strength Vitamin C: May reduce effectiveness or cause redness
Possible Side Effects of Mandelic Acid
- Mild dryness
- Flaking on thin skin areas
- Tingling sensation during initial uses
If symptoms persist beyond 7 days or worsen, discontinue use and consult a dermatologist.
FAQs
- What is Mandelic Acid and how does it work on the skin?
→ It’s an AHA derived from bitter almonds that gently exfoliates, reduces acne, and brightens skin tone.
- What is Mandelic Acid and how does it work on the skin?
- Is Mandelic Acid suitable for sensitive skin?
→ Yes. Its large molecules penetrate slowly, reducing irritation, making it great for sensitive skin.
- Is Mandelic Acid suitable for sensitive skin?
- How often should I use Mandelic Acid each week?
→ Beginners: 2–3 times/week, then increase based on tolerance.
- How often should I use Mandelic Acid each week?
- Can Mandelic Acid be combined with other acids?
→ Yes, it can be combined with BHA or Lactic Acid, but use on alternate days or at low concentrations to avoid irritation.
- Can Mandelic Acid be combined with other acids?
- Can Mandelic Acid cause dryness or flaking?
→ Mild dryness or flaking may occur at first, so pair it with a good moisturizer.
- Can Mandelic Acid cause dryness or flaking?
- How is Mandelic Acid different from Glycolic Acid and Lactic Acid?
→ They differ in molecular size, penetration rate, and irritation potential. Mandelic Acid is gentler and better for sensitive skin.
- How is Mandelic Acid different from Glycolic Acid and Lactic Acid?
Conclusion
Mandelic Acid is an excellent choice for those new to chemical exfoliation but worried about irritation. With its ability to improve acne, brighten skin, fight aging, and suit sensitive skin, this acid deserves a place in your skincare routine. To achieve the best results, start with a low concentration, pair with moisturizers, and always use sunscreen.


